I once stared at account statements on a quiet night and felt the weight of a big choice. That feeling is familiar for many people who watch their money grow and worry about the path ahead.
Paper assets — like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds — offer clear records and easy access. They let investors automate contributions through employer plans and IRAs and scale holdings over years.
So the core question arrives: “Is it smart to keep all my retirement savings in paper assets?” This guide previews both sides. Benefits include liquidity and broad diversification. Drawbacks include volatility and sequence risk when markets drop early in retirement.
The Schwab 4% framework gives a starting level for spending, but real planning must adapt each year for taxes, cost shifts, and changing rates. The stock market has rewarded patience, yet the exact mix of funds and investments matters for long-term results.
Key Takeaways
- Paper-asset portfolios are transparent and easy to automate.
- Diversification helps, but market swings create sequence risk.
- Use a flexible planning approach rather than rigid rules.
- Fees, taxes, and rates affect income over many years.
- Personal goals and mix of funds should guide withdrawals.
What “paper assets” mean for U.S. retirement planning today
Knowing where your securities sit matters as much as which ones you own.
Paper assets are tradable securities such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, and cash equivalents. These types let investors mix growth, stability, and short-term liquidity within a single portfolio.
Core definitions
Stocks offer growth. Bonds provide income and stability. Mutual funds and ETFs package diversified baskets, lowering cost and effort for long-term market exposure.
Where they live
Common homes include employer plans (401(k), Roth 401(k)), IRAs (traditional and Roth), HSAs, and taxable brokerage accounts. Roth options can offer tax-free withdrawals, and SECURE 2.0 removed RMDs for Roth 401(k)s this year.
“Place assets where tax rules and access match your goals.”
| Account | Primary use | 2025 limits / notes | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401(k) / Roth 401(k) | Employer deferrals | $23,500; $31,000 with catch-up; super catch-up up to $34,750 (60–63) | High deferrals, employer match |
| IRA / Roth IRA | Individual tax-advantaged savings | $7,000; $8,000 with catch-up; Roth phase-outs based on MAGI | Supplemental tax planning |
| HSA | Health-focused triple tax advantage | Contribution limits vary; can invest in funds | Medical cost planning |
| Brokerage accounts | Taxable market access | No contribution limit | Extra investing after tax-advantaged limits |
- Use equities for growth, bonds for balance, cash-like vehicles for near-term needs.
- Asset location across accounts can improve after-tax results.
The upside: liquidity, growth potential, and low costs in the stock market
Over decades, disciplined investing in broad funds can turn modest deposits into meaningful income.
Compounding and long-term growth
Regular contributions into diversified stock market funds let compound returns work. Even modest monthly deposits can grow substantially over many years. Stocks provide future growth potential that supports later-year spending, while bonds and cash add stability.
Diversification with index funds and mutual funds
Low-cost index funds and mutual funds offer broad exposure across sectors and regions. That lowers single-stock risk and keeps fees small so more money stays invested.
“Automatic investing and low fees help discipline and long-term results.”
- Liquidity in paper markets lets you rebalance or raise cash quickly.
- Simple index types cover domestic, international, and small-cap exposure without complex selection.
- As retirement nears, shift from aggressive mixes toward balanced allocations to protect lifestyle spending.
| Feature | Benefit | How it helps |
|---|---|---|
| Index funds | Low fees, broad reach | Higher net growth over years via reduced expense drag |
| Mutual funds | Active or passive choices | Targeted exposure with professional management |
| Market liquidity | Quick access | Reallocate or withdraw without sale restrictions |
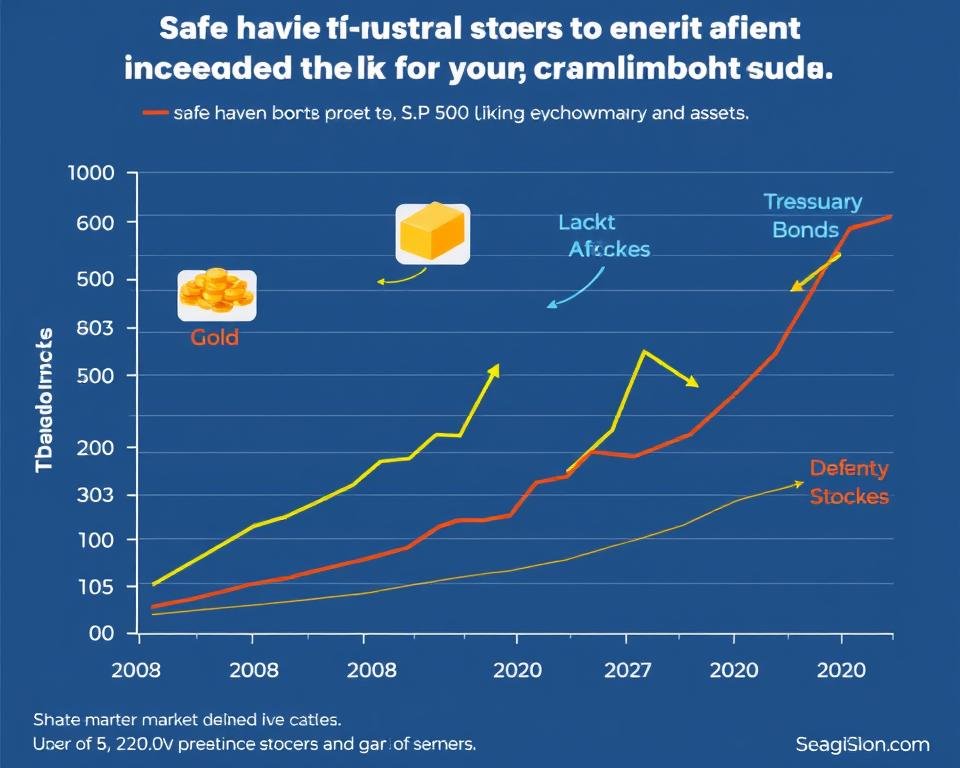
The downside: volatility, sequence risk, and interest rate sensitivity
Market downturns and rising rates can change a comfortable plan into a stressful one overnight.
Sequence-of-returns risk means poor early-year market returns while withdrawals start can shrink a portfolio much faster than average returns suggest.
That damage can be permanent and may force spending cuts or risky selling. Retirees should expect variability in year-to-year value and plan accordingly.
How interest rates affect bond values and income stability
When rates climb, bond prices fall. Funds that hold long-duration bonds lose value faster. Schwab warns fixed income faces principal loss during rate rises and other risks like credit and liquidity.
Bond mutual funds and ETFs trade daily, so their market value moves with rates and credit changes. Match duration and credit quality to your spending horizon.
“Hold enough cash for near-term needs and diversify bond holdings to reduce shocks.”
- Keep cash for 1–3 years of spending.
- Diversify across short-duration and higher-quality funds.
- Rebalance and set conservative withdrawal levels.
| Risk | Impact | Practical step |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence-of-returns | Early losses reduce longevity | Cash cushion; lower initial withdrawals |
| Rising rates | Bond fund value drops | Shorten duration; diversify credit |
| Market volatility | Emotional pressure; forced sales | Rebalance rules; realistic expectations |
Is it smart to keep all my retirement savings in paper assets?
Deciding how much to leave in market-traded holdings shapes both risk and flexibility for a retirement plan.
Concentration risk versus a balanced strategy
Convenience and liquidity are real benefits of holding public market holdings. Trading is easy and low-cost funds scale well for long-term growth.
But relying on a single asset type raises concentration risk. A big drop early in withdrawals can harm longevity.
When most holdings in markets make sense — and when they don’t
Keeping most money in public funds suits investors with long time horizons, high risk tolerance, and access to diversified, low-cost index funds.
That approach poorly fits those with near-term cash needs, low tolerance for swings, or limited guaranteed income sources like pensions.
“Diversify across stocks, bonds, and cash, and choose a mix you can live with during bear markets.”
- Stress-test plans and set rebalancing rules.
- Hold 1–3 years of spending in defensive reserves to avoid forced sales.
- Integrate Social Security timing and other income to lower market pressure on savings.
Summary: Most retirement savings can remain in market investments when diversified and flexible. Going all into one risk bucket rarely proves optimal.
Building a resilient asset allocation for retirement income
Designing a resilient mix of holdings starts with clear roles for cash, bonds, and stocks.
Mixing stocks, bonds, and cash to support near-term withdrawals
Bucketing sets aside cash and short-term bond funds for 1–2 years of expenses. This reduces pressure to sell after a market drop and supports steady income while you ride out volatility.
Use diversified, low-cost funds for core sleeves. Keep equities for long-term growth and bonds for ballast. That balance helps when taking withdrawals during down markets.
Adjusting your allocation as you age to manage downside risk
Start with a conservative-to-moderate glide path. Example mixes: Conservative (Cash 30%, Bonds 50%, Large-Cap 15%, International 5% — return 5.04%, SD 4.40%), Moderately Conservative (return 5.90%, SD 7.28%), Moderate (return 6.53%, SD 10.01%).
“Each part of your portfolio should have a job: cash for stability, bonds for ballast, equities for growth.”
- Rebalance on a schedule: trim winners, add to laggards to enforce buy-low discipline.
- Tie allocation to time horizons: cash 1–2 years, bonds 3–5 years, stocks for later years and inflation protection.
- Monitor variability using standard deviation conceptually to set realistic expectations.
Withdrawal strategies: from the 4% rule to flexible spending
Deciding how much to take each year affects how long your portfolio lasts. Use a rule as a starting place, then adapt when markets or life change.

Core assumptions behind the 4% guideline
The classic rule: withdraw 4% of the portfolio in the first year (for example, $40,000 from $1,000,000) and raise that amount each subsequent year for inflation.
What that assumes: a 50/50 stock-bond split, roughly a 30-year horizon, and high historical success rates. It does not include specific taxes, fees, or unique life events.
Making flexible adjustments when markets move
Rather than a fixed inflation bump, cut withdrawals modestly after poor market years and allow increases when balances recover.
Set guardrails — for example, cap increases at a modest percent and avoid cuts below a floor. Review spending annually and stress-test several sequential weak years.
Coordinate withdrawals with guaranteed income
Blend withdrawals with Social Security, pensions, and annuities to smooth cash flow and manage taxes. Plan which accounts to draw from first to optimize after-tax income and preserve balance across funds.
“A personalized, flexible withdrawal plan supports confidence across market cycles.”
| Rule | Typical assumption | Practical tweak |
|---|---|---|
| 4% starting withdrawal | 50/50 stocks-bonds; 30 years | Use as baseline; adjust for taxes and fees |
| Dynamic spending | Responds to portfolio returns | Cut modestly after down years; raise when recovered |
| Guardrails | Min/max annual change | Protect real income and portfolio longevity |
Taxes and account strategy: Roth, traditional, brokerage, and HSAs
How you place funds across accounts often matters more than the funds themselves.
Map accounts to tax roles: use Roth accounts for potential tax-free growth, traditional accounts for deferral, and brokerage accounts for flexibility and favorable capital gains treatment.
Required minimum distributions and annual impact
Required minimum distributions from traditional accounts force taxable withdrawals that affect tax brackets and Medicare IRMAA. Roth 401(k)s no longer have RMDs starting this year.
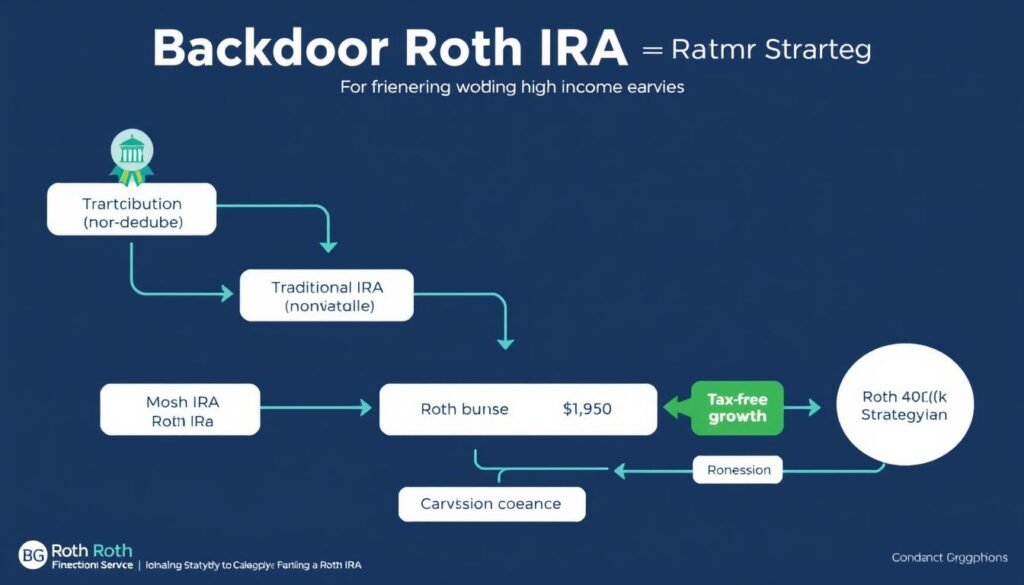
Roth options, catch-ups, and the mega backdoor Roth
2025 contribution limits matter: 401(k) $23,500 plus $7,500 catch-up; IRAs $7,000 plus $1,000 catch-up. Beginning 2026, some catch-ups must go to Roth for high earners. A mega backdoor Roth can work if plan rules permit after-tax contributions and in-service rollovers.
Capital gains, asset location, and brokerage accounts
Long-term capital gains rates (0%, 15%, 20%) affect taxable sell decisions. Place income-generating bond funds in tax-deferred accounts and high-growth funds in Roth. Use ETFs or munis in brokerage accounts to lower tax drag.
HSAs for healthcare and tax efficiency
HSAs (2025: $4,300 individual/$8,550 family; $1,000 catch-up 55+) offer a triple tax advantage, no RMDs, and penalty-free non-medical withdrawals at 65 (taxable). They act as flexible savings accounts for medical costs and Medicare premiums.
“Coordinate withdrawals across accounts to manage brackets and preserve long-term income.”
- Plan conversions and withdrawals with yearly tax review.
- Use brokerage liquidity and tax-loss harvesting when helpful.
- Place growth where tax-free compounding helps most.
| Account | Best tax role | 2025 note |
|---|---|---|
| Roth IRA / Roth 401(k) | Tax-free growth | Roth 401(k) RMD removal this year |
| Traditional 401(k) / IRA | Tax deferral | Subject to required minimum distributions |
| Brokerage accounts | Liquidity & capital gains planning | Good for ETFs, munis; supports tax-loss harvesting |
For withdrawal sequencing and tax-aware rules, see our guide on tax-smart withdrawals.
Interest rates, inflation, and planning through market changes
Markets move in cycles, and planning that assumes change keeps options open.
Rising interest rates push bond prices down and can pressure long-duration funds. Shorter-duration bond funds lose less value when rates climb, while longer-duration holdings may suffer larger drops.
When rates fall, long-duration bonds often gain value and can boost portfolio returns. Equity valuations also shift with rate swings as discount rates change, which affects near-term portfolio value and income expectations over several years.
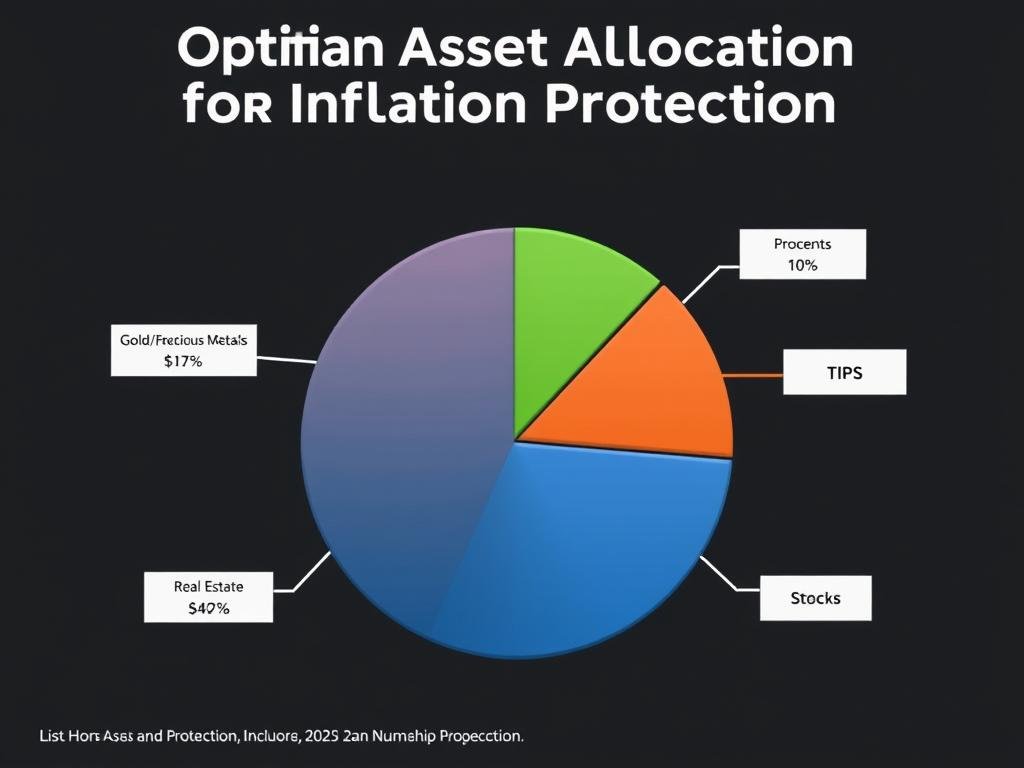
Inflation erodes purchasing power. Holding a mix of funds, including equities, helps preserve real value over time. Equities tend to offer better long-run protection against rising prices than cash or short-term bonds.
Plan for changes: stress-test allocation and withdrawal rules across scenarios of high and low inflation. Use forward-looking return and risk assumptions rather than relying only on past averages.
“Document rules for adjustments so you’re ready before markets shift.”
- Shorten duration when higher rates are expected; lengthen when declines seem likely.
- Rebalance after big moves to realign risk and capture opportunities.
- Coordinate trading with tax plans—capital gains brackets matter during regime shifts.
- Diversify across asset classes and geographies to reduce localized shocks.
| Factor | Effect | Practical step |
|---|---|---|
| Rising interest rates | Bond fund values fall; equity multiples may compress | Trim long-duration bonds; hold cash for near-term needs |
| Falling interest rates | Long-duration bonds gain; yields drop for new capital | Consider laddering and locking select yields |
| Higher inflation | Real value of money declines | Keep growth-oriented investments; tie withdrawals to inflation gauges |
Best practices checklist to keep money working while managing risk
A clear set of steps keeps money working while you manage downside risk.
Automate contributions so deposits flow into diversified funds on schedule. This turns market swings into disciplined dollar-cost averaging and saves time.
Maximize tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s, IRAs, and HSAs. Coordinate catch-ups when eligible to accelerate retirement savings and reduce taxable income.
Rebalance regularly on a cadence or threshold. Trim overweight sectors and add to laggards to control risk and enforce buy-low behavior.
More practical moves
Use low-cost index funds for core exposure and add only purposeful satellites. Keep a 1–2 year reserve in cash or short-term bonds to avoid selling during downturns.
Practice tax-smart habits: asset location, tax-loss harvesting in taxable accounts, and mindful gain realization to manage brackets and taxes.
“Schedule annual planning check-ins and track progress against milestones rather than market noise.”
- Keep paperwork and tools organized: contribution schedules, RMD timelines, Social Security decisions.
- Consider a fiduciary advisor for accountability and to refine strategy as rules and markets change.
| Action | Why it helps | When | Quick tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automate deposits | Keeps money working steadily | Start now | Set monthly transfers |
| Max tax accounts | Lower taxes, faster capital growth | Each tax year | Prioritize employer match |
| Rebalance | Controls risk; enforces discipline | Annually or 5% drift | Use auto-rebalance if available |
| Maintain reserve | Avoid forced sales in down markets | Before retirement | Hold 1–2 years of expenses |
Conclusion
An organized approach helps convert market potential into steady income.
Use simple building blocks: core index funds for growth, bonds and cash for near-term protection, and tax-aware account placement to lower costs and manage required minimum distributions.
Favor flexible withdrawal rules that tie the amount withdraw to portfolio value, returns, and expenses. Revisit allocation when interest rates or inflation shift value across types.
Keep contributions regular, document guardrails for taking withdrawals, and simplify tools so decisions stay disciplined during stress. For background on policy and account roles, see public policy on retirement accounts.
Practical takeaway: let diversified funds work over time, adapt plans as conditions change, and get help when choices affect long-term income and taxes.
FAQ
What do “paper assets” include for U.S. retirement planning today?
Paper assets refer to holdings such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, and cash equivalents. These live inside 401(k)s, traditional and Roth IRAs, HSAs, and taxable brokerage accounts. Each account type has distinct tax rules, contribution limits, and withdrawal requirements that shape how you use those holdings for income.
Why do many investors favor funds and ETFs for long-term growth?
Funds and ETFs offer broad exposure, low operating costs, and the power of compounding over decades. Index funds track markets and reduce single-stock risk, while diversified mutual funds and ETFs help build a predictable growth path with modest fees, making them popular building blocks for retirement portfolios.
How does diversification with index funds help manage risk?
Diversification spreads exposure across sectors, countries, and asset classes. Index funds lower the impact of any single company or sector underperforming, which smooths returns and reduces volatility compared with concentrated stock holdings. That balance tends to improve long-term outcomes for retirees.
What are the main risks of holding primarily market-based paper assets?
Key risks include market volatility, sequence-of-returns risk during early withdrawals, interest-rate sensitivity for bond values, and concentrated exposure to a single sector or employer stock. These risks can erode portfolio value when you need income most.
How do interest rates affect bond values and retirement income?
When interest rates rise, existing bond prices typically fall because new bonds pay higher coupons. That can reduce portfolio value for bond-heavy retirees. Conversely, rising rates can offer better yields for new bond purchases or short-term cash instruments, improving income options over time.
Should I place most or all retirement funds in market-based paper holdings?
Holding a large share in market assets can make sense for younger savers with long horizons, but retirement needs more balance. Concentration risk rises near and during retirement. A blend of stocks, bonds, and cash-like instruments helps protect income and reduce withdrawal volatility.
When does keeping most assets in markets make sense, and when does it not?
It makes sense when you have a long time horizon, strong emergency savings, and a plan to delay large withdrawals. It’s less appropriate if you expect near-term spending, lack guaranteed income, or cannot tolerate sharp portfolio declines. Personal goals and time to the first withdrawal dictate the mix.
How should I mix stocks, bonds, and cash to support near-term withdrawals?
Keep one to three years of living expenses in cash or short-term bonds to avoid selling into downturns. Allocate the remainder between stocks for growth and longer-term bonds for stability. The exact split depends on risk tolerance, withdrawal needs, and overall portfolio size.
How should allocation change as I age to limit downside risk?
Gradually shift toward more income-producing and stable assets as retirement nears. Many retirees reduce equity exposure and increase bond or laddered fixed-income holdings. Adjustments should be gradual to preserve growth potential while lowering volatility.
What does the 4% rule assume about portfolio mix and time horizon?
The 4% rule assumes a balanced portfolio—commonly 50–75% stocks and the rest bonds—designed to last roughly 30 years. It’s a guideline, not a guarantee; market conditions, inflation, and spending needs can require adjustments.
How can I use flexible withdrawal strategies when markets change?
Reduce withdrawals after large market drops, tap cash reserves instead, or use a guardrail system that adjusts spending based on portfolio performance. Flexibility preserves longevity and reduces the risk of depleting assets during prolonged downturns.
How do Social Security and other income sources fit withdrawal planning?
Coordinate withdrawals with guaranteed income like Social Security, pensions, and annuities. Delaying Social Security can increase lifetime benefits, lowering portfolio withdrawal pressure. Use tax-aware withdrawal sequencing to minimize total taxes.
What role do required minimum distributions (RMDs) play in retirement withdrawals?
RMDs force withdrawals from traditional IRAs and employer plans starting at the required age, increasing taxable income. Roth IRAs do not have RMDs for original owners, which can aid tax planning. Factor RMDs into your cash-flow and tax strategies to avoid surprises.
When should I consider Roth conversions, catch-up contributions, or a mega backdoor Roth?
Consider Roth conversions in lower-income years to lock in tax-free growth, use catch-up contributions when eligible to boost savings, and explore the mega backdoor Roth if your 401(k) allows after-tax contributions and in-plan conversions. These tools help manage taxable income later and reduce future RMD impact.
How do capital gains and asset location affect taxes in retirement?
Place assets strategically: tax-inefficient investments like taxable bonds often work best in tax-deferred accounts, while tax-efficient equities fit well in taxable brokerage accounts. Managing capital gains timing and tax-loss harvesting can lower annual tax bills.
Can HSAs help with healthcare costs in retirement?
Yes. HSAs offer triple tax benefits: tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses. They’re a powerful tool for covering healthcare costs and reducing taxable income if used over time.
How should I plan for inflation and changing interest rates?
Build inflation protection with equities, TIPS, and real assets, and ladder bonds to manage rate changes. Review assumptions regularly and stress-test your plan under higher inflation or prolonged low-growth scenarios to ensure income stays on track.
What are best-practice actions to keep money working while managing risk?
Automate savings, max out tax-advantaged accounts when possible, rebalance annually, and maintain an emergency cash buffer. Regularly review asset allocation, tax strategies, and beneficiary designations to keep the plan aligned with changing needs.















































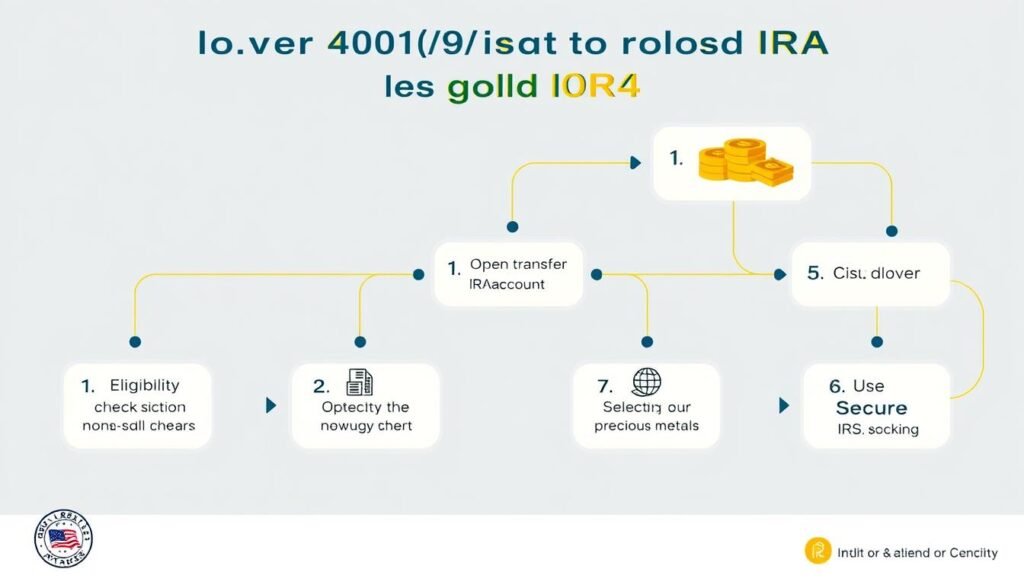
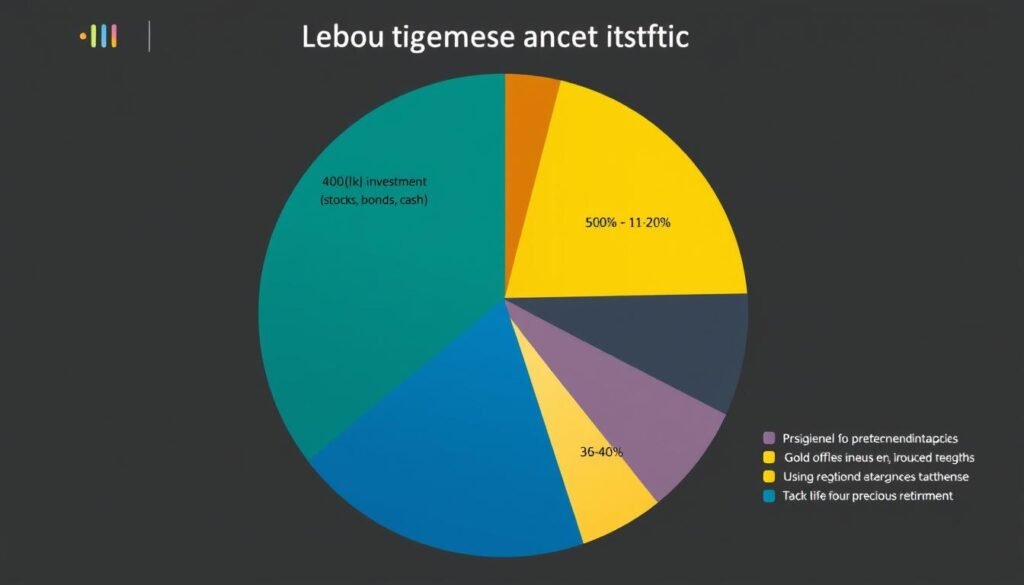






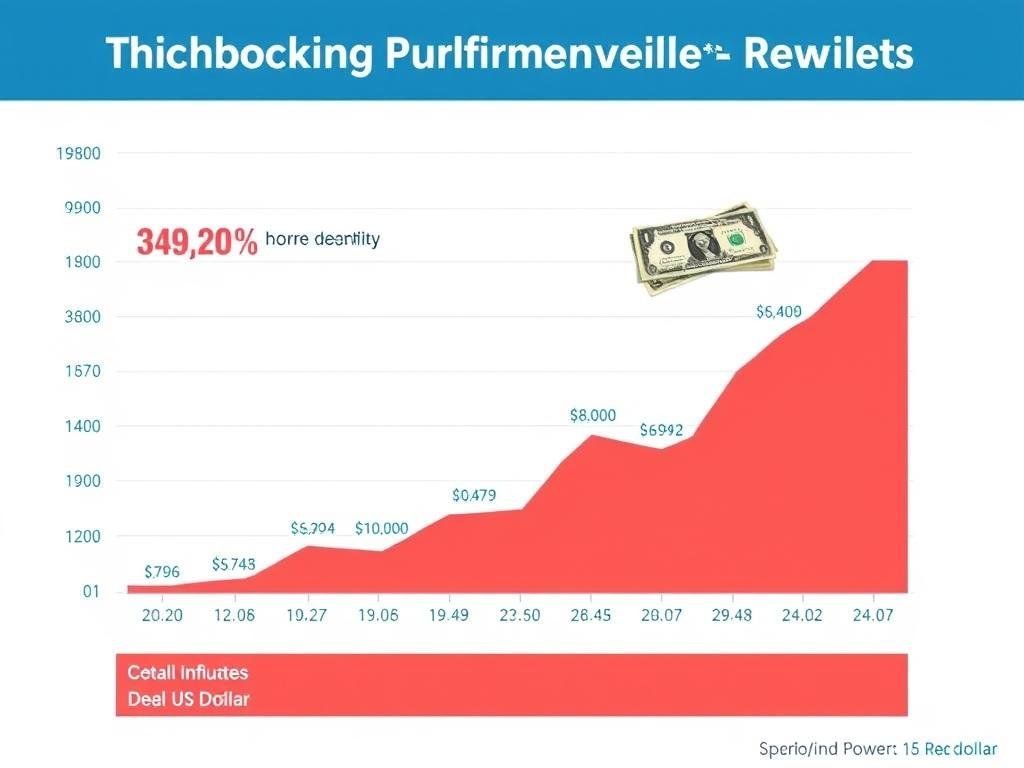






































Strategy #3: Optimize Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits represent a critical income stream that can help your retirement money last. The timing of when you claim these benefits can significantly impact your lifetime income.
While you can start collecting Social Security at age 62, your benefits increase approximately 8% for each year you delay claiming until age 70. This guaranteed return is hard to beat in today’s investment environment.
Real-life scenario: Consider a retiree eligible for a $1,500 monthly benefit at full retirement age (66). If they claim at 62, they’ll receive only $1,125 per month. But if they wait until 70, their monthly benefit grows to $1,980 – a 76% increase over the age 62 amount. Over a 25-year retirement, this difference adds up to more than $250,000 in additional benefits!
For married couples, coordinating Social Security claiming strategies becomes even more important. The higher-earning spouse might delay benefits until 70, while the lower-earning spouse claims earlier. This approach maximizes the survivor benefit, which is based on the higher earner’s benefit amount.
Think of Social Security as the foundation of your retirement income house. The stronger this foundation, the more secure your overall financial structure will be, helping your retirement money last throughout your lifetime.