For high-income earners, choosing between a Roth 401(k) and a traditional 401(k) can significantly impact your retirement savings and tax situation. While both plans offer valuable tax advantages, they work in fundamentally different ways—and the best choice depends on your specific financial circumstances, current tax bracket, and retirement expectations.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key differences between these retirement plans and provide strategies to optimize your retirement savings as a high-income earner. We’ll explore tax implications, contribution limits, and practical scenarios to help you make an informed decision.
Key Differences Between Roth 401(k) and Traditional 401(k)
Tax Treatment: Pre-Tax vs. After-Tax Contributions
The fundamental difference between these retirement plans lies in when you pay taxes:
Traditional 401(k)
Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your current taxable income. For example, if you earn $200,000 and contribute $23,500, you’ll only be taxed on $176,500 of income for that year.
However, you’ll pay ordinary income tax on both your contributions and earnings when you withdraw funds in retirement.
Roth 401(k)
Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you pay taxes on that money now. Your $23,500 contribution comes from income that’s already been taxed.
The significant advantage is that qualified withdrawals in retirement—including all earnings—are completely tax-free.
2025 Contribution Limits
| Feature | Traditional 401(k) | Roth 401(k) |
| Basic Contribution Limit | $23,500 | $23,500 |
| Catch-up Contribution (Age 50-59) | $7,500 | $7,500 |
| Super Catch-up Contribution (Age 60-63) | $11,250 | $11,250 |
| Total Annual Limit (including employer contributions) | $70,000 | $70,000 |
Both plans share the same contribution limits, allowing high-income earners to save substantial amounts for retirement regardless of which option they choose.
Income Limits for Eligibility
Unlike Roth IRAs, which have income limits that prevent high earners from contributing directly, Roth 401(k) plans have no income restrictions. This makes them particularly valuable for high-income professionals who want the benefits of tax-free growth but are ineligible for Roth IRAs.

Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
As of 2024, a significant change benefits Roth 401(k) holders:
- Traditional 401(k): You must begin taking RMDs at age 73 (or age 75 starting in 2033), regardless of whether you need the money.
- Roth 401(k): No RMDs are required during your lifetime, giving you greater flexibility in retirement planning and potential for continued tax-free growth.
This RMD difference can be particularly advantageous for high-income earners who may not need to draw from retirement accounts immediately and wish to maximize tax-free growth or leave tax-advantaged assets to heirs.
Special Considerations for High-Income Earners
Current vs. Future Tax Brackets
The central question for high-income earners is whether your tax rate will be higher or lower in retirement compared to your working years.
When Traditional 401(k) May Be Better
- You expect to be in a lower tax bracket during retirement
- You’re currently in one of the highest tax brackets (35% or 37%)
- You need to reduce your current taxable income
- You want to maximize current tax deductions
When Roth 401(k) May Be Better
- You expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement
- You believe overall tax rates will increase in the future
- You want to maximize tax-free income in retirement
- You want to leave tax-free assets to heirs
For many high-income earners, current tax rates are at historic lows, and there’s concern that rates may increase in the future due to growing national debt and changing fiscal policies. This uncertainty makes Roth contributions appealing despite the higher current tax cost.
Employer Match Considerations
An important note for high-income earners: employer matching contributions always go into a traditional pre-tax account, even if you make Roth contributions. This creates automatic tax diversification in your retirement portfolio.
Example: If you contribute $20,000 to your Roth 401(k) and receive a $10,000 employer match, your retirement account will contain $20,000 in Roth funds and $10,000 in traditional pre-tax funds.
Backdoor Roth Strategies for Ultra-High Earners
For ultra-high-income earners who want to maximize tax-advantaged retirement savings, combining a Roth 401(k) with backdoor Roth IRA contributions can be powerful:
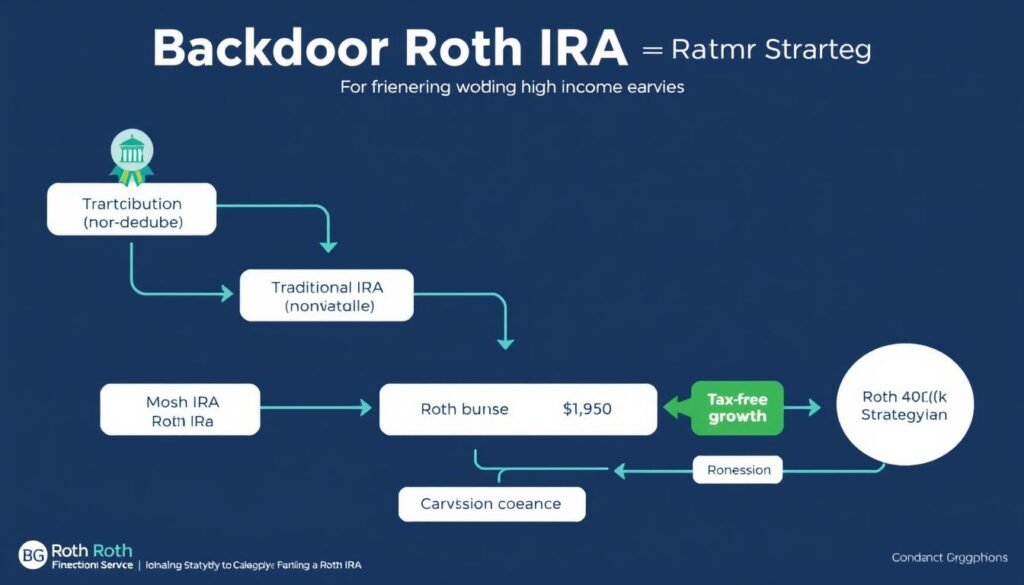
- Contribute the maximum to your Roth 401(k) ($23,500 in 2025, plus catch-up contributions if eligible)
- Make a non-deductible contribution to a traditional IRA ($7,000 in 2025, plus $1,000 catch-up if over 50)
- Convert the traditional IRA to a Roth IRA (the “backdoor” method)
- Result: Up to $31,500 in Roth contributions annually ($42,750 if age 60-63), plus employer match
This strategy works best for those without existing pre-tax IRA balances due to the pro-rata rule for conversions. Consult with a tax professional before implementing this approach.
Case Studies: Roth vs. Traditional for High-Income Scenarios
Case Study 1: $250,000 Earner in California
Profile: Sarah, 45, earns $250,000 as a technology executive in California. She’s in the 35% federal tax bracket plus 9.3% state tax.
Analysis:
- Traditional 401(k): Saves approximately $10,400 in taxes this year on a $23,500 contribution
- Roth 401(k): Costs $10,400 more in taxes this year but provides tax-free withdrawals in retirement
Recommendation:
A hybrid approach makes sense for Sarah. She should contribute enough to the traditional 401(k) to reduce her taxable income below the 35% federal bracket threshold, then direct remaining contributions to the Roth 401(k). This balances current tax savings with future tax-free growth.
Case Study 2: $500,000 Earner with Variable Income
Profile: Michael, 52, earns $500,000 annually as an investment banker, with significant variability in his bonus income. He’s in the 37% federal tax bracket.

Analysis:
- Traditional 401(k): Provides substantial current tax savings at the 37% bracket
- Roth 401(k): Higher current tax cost but creates tax diversification
Recommendation:
Michael should use a strategic timing approach. In years with exceptionally high bonuses, maximize traditional 401(k) contributions to reduce taxable income. In lower-income years, prioritize Roth 401(k) contributions when the tax impact is less severe. At age 52, he should also take advantage of the $7,500 catch-up contribution.
Strategic Recommendations for High-Income Earners
When to Prioritize Roth 401(k) Contributions
Consider prioritizing Roth 401(k) contributions when:
- You’re early in your career with expectations of significantly higher future earnings
- You have substantial taxable investment accounts and want to increase tax-free assets
- You don’t need the current tax deduction to meet other financial goals
- You want to hedge against future tax rate increases
- You want to eliminate RMDs from your retirement planning concerns
- You’re interested in estate planning and want to leave tax-free assets to heirs
When to Stick with Traditional 401(k) Contributions
Traditional 401(k) contributions may be more advantageous when:
- You’re at your peak earning years and in the highest tax brackets
- You need to reduce current taxable income to qualify for other tax benefits
- You anticipate being in a significantly lower tax bracket in retirement
- You’re nearing retirement with limited time for tax-free growth to offset the upfront tax cost
- You plan to retire in a state with no income tax (from a high-tax state)
Hybrid Approaches for Tax Diversification
For many high-income earners, the optimal strategy involves tax diversification:
“Tax diversification is like investment diversification—it reduces risk by giving you options. Having retirement funds in different tax buckets allows you to optimize withdrawals based on your tax situation each year in retirement.”
Consider these hybrid approaches:
- Split contributions: Divide your annual contributions between traditional and Roth accounts
- Strategic timing: Use traditional contributions in high-income years and Roth in lower-income years
- Bracket management: Use traditional contributions to reduce income to a lower tax bracket, then switch to Roth
- Age-based shifting: Start with traditional early in your career, then gradually shift toward more Roth contributions as retirement approaches
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I contribute to both a Roth 401(k) and a traditional 401(k)?
Yes, you can split your contributions between both types of accounts as long as your total contributions don’t exceed the annual limit ($23,500 in 2025, plus catch-up contributions if eligible). This strategy creates tax diversification in your retirement portfolio.
What if I exceed IRS income limits for retirement contributions?
Unlike Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k) plans have no income limits, making them accessible to high-income earners regardless of compensation level. However, all 401(k) plans are subject to annual contribution limits and potential restrictions for highly compensated employees depending on your company’s plan structure.
How are employer matches treated in a Roth 401(k)?
Employer matching contributions always go into a traditional pre-tax account, even if you make Roth contributions. This means employer matches will be taxable upon withdrawal in retirement. This creates automatic tax diversification in your retirement savings.
Can I convert my existing traditional 401(k) to a Roth 401(k)?
Some employer plans allow in-plan Roth conversions, but this varies by plan. If permitted, you’ll pay ordinary income tax on the converted amount in the year of conversion. For high-income earners, this can result in a substantial tax bill, so careful planning is essential.
How does the Secure 2.0 Act affect Roth 401(k) planning?
The Secure 2.0 Act eliminated RMDs for Roth 401(k) accounts starting in 2024, making them even more attractive for high-income earners. The legislation also introduced higher catch-up contribution limits for those aged 60-63 beginning in 2025, allowing for increased Roth savings during pre-retirement years.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Situation

The choice between a Roth 401(k) and a traditional 401(k) for high-income earners isn’t simply about math—it’s about creating flexibility and security in your retirement planning. While traditional 401(k)s offer immediate tax benefits, Roth 401(k)s provide tax-free growth and withdrawals that can be invaluable in retirement.
For most high-income earners, a strategic combination of both account types creates the optimal tax diversification strategy. This approach gives you flexibility to manage your tax situation throughout retirement and adapt to changing tax laws and personal circumstances.
Remember that retirement planning is highly personal, and the best strategy depends on your unique financial situation, career trajectory, and retirement goals. Consulting with a qualified financial advisor who specializes in retirement planning for high-income professionals can help you develop a customized approach that maximizes your retirement savings while minimizing your lifetime tax burden.
Get Personalized Retirement Planning Advice
Uncertain which retirement strategy is optimal for your high-income situation? Our team of financial advisors specializes in tax-efficient retirement planning for professionals earning $150,000+. Schedule a complimentary consultation to develop a customized strategy that maximizes your retirement savings.













































